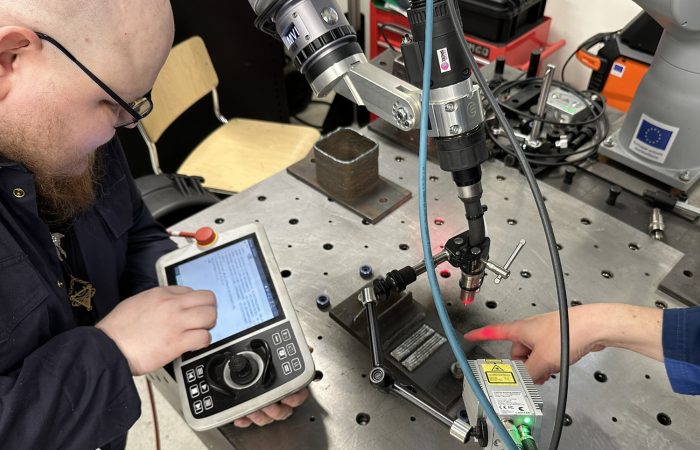
We Research: Mobile robotics and exoskeletons are transforming work in industry
RoboFleet, an ongoing project at RoboAI Industry, focuses on the study of mobile robotics, exoskeletons, and the efficient use of their fleets in modern production. The main focus of the research is on the industrial use of these technologies and new potential applications in Satakunta's SME sector. The sustainability of human capital and the availability of skilled labour are key issues in today's western manufacturing economy. There is a need to retain skilled staff and new ways of making existing jobs more efficient are constantly being sought.
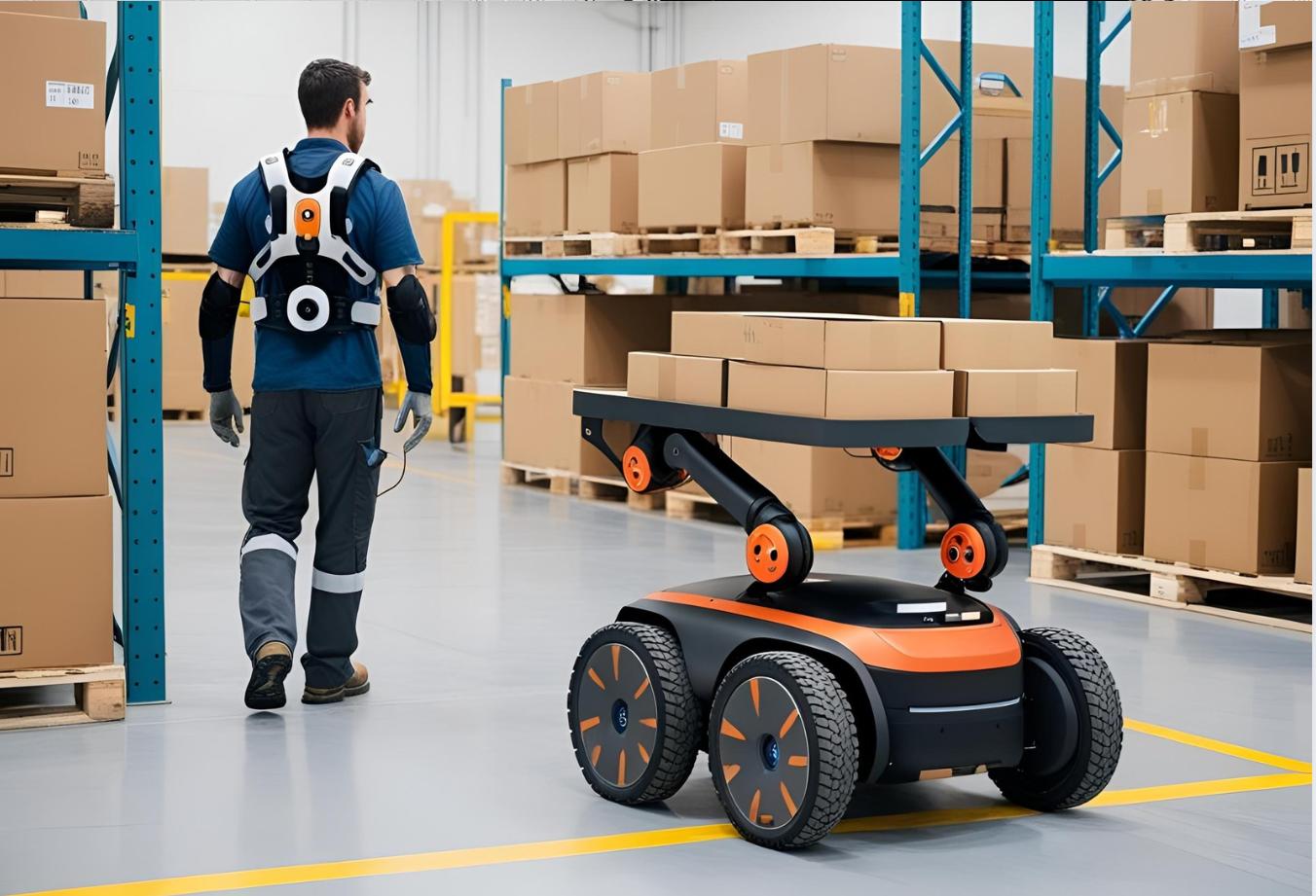

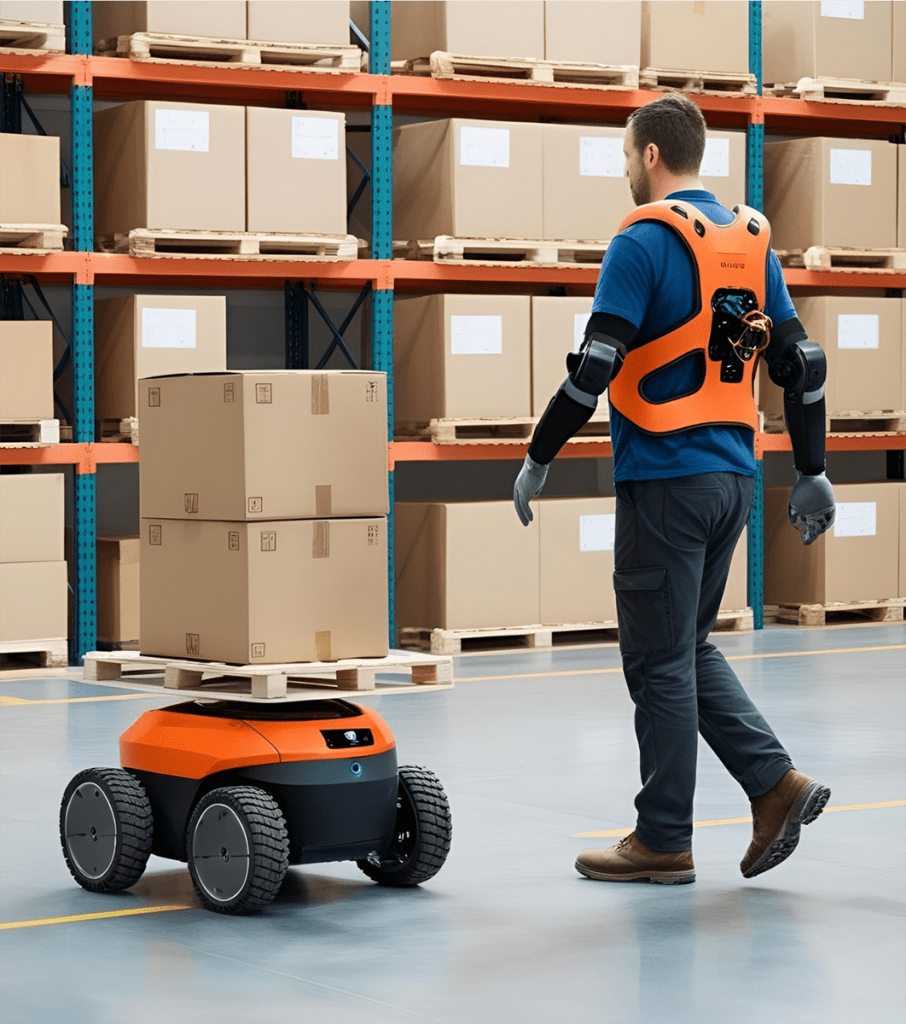
Mobile robotics aims to transfer time-consuming but unproductive tasks - such as various logistics tasks - to robots. This will reduce the workload of workers and free up resources for more productive work. A wide range of areas for development will be identified, and the aim is to use robotics in a variety of ways, from monitoring tasks to picking up goods.
Throughout history, efforts have been made to reduce the strain of muscular work by using machines, but there are still certain tasks that are best suited to human beings. Now widely marketed, wearable supports, or exoskeletons, aim to reduce both static and dynamic loads on the body. The use of these still relatively unknown aids to improve well-being and productivity will be explored through user experience in a variety of jobs.
In the future, more and more automated, remotely connected robots and machines will operate in our environment. There is therefore a clear need to be able to control their operation centrally. Fleet management software is being developed by both robot manufacturers and independent software companies. The idea is to control the interaction of different robots from different robot manufacturers in an optimised way, so that the fleet management software generates, for example, the best possible driving sequences. There are several applications available and we are investigating their usability and reliability.
The RoboFleet project has two components, one focused on applied research and one dedicated to the acquisition of test equipment. Investments will be made in a new type of mobile robotics, with the aim of advancing research on mobile robots capable of moving in challenging terrain in open spaces. Another major area of mobile investment is in humanoid robots that walk on two legs and are similar to humans, whose current development is gaining a lot of visibility worldwide.
Exoskeleton procurement aims to find a wide range of passive and active models suitable for different types of tasks. This will enable the project to carry out a wide range of experiments in different work tasks.
The research work will be based on RDI cases with companies, with the aim of finding new technical solutions to the problems identified. Researchers and company representatives work together to define the problem to be studied, followed by a series of experiments to identify the best approach.
After the experimentation phase, the testing phase is moved on, usually starting with a trial of the chosen technology in the RoboAI laboratory. If the method is found to work under laboratory conditions, the next experiment will be carried out on the company's premises. In this way, potential uncertainties are more present and more detailed research data on the practical implementation can be obtained. At the same time, both parties will also gain valuable additional insights into the cooperation between the educational institution and the business world.
 Did you know?
Did you know?
- Mobile robots are autonomously mobile robots, most commonly powered by batteries. They are already widely used for a variety of social tasks, from mowing the lawn to carrying shopping bags. Increasingly diverse tasks may in future be delegated to autonomous decision-making models.
- Exoskeletons are wearable technologies that reduce muscle and joint stress. These external scaffolds can provide assistance passively, e.g. through spring force and additional support, or actively, e.g. through batteries and servo motors.
- Fleet management refers to software that manages the tasks of several robots. These control the operation of higher levels of equipment, such as traffic and task scheduling. The aim is to integrate equipment from different manufacturers into a single entity that can be modelled and controlled.
 Did you know?
Did you know?